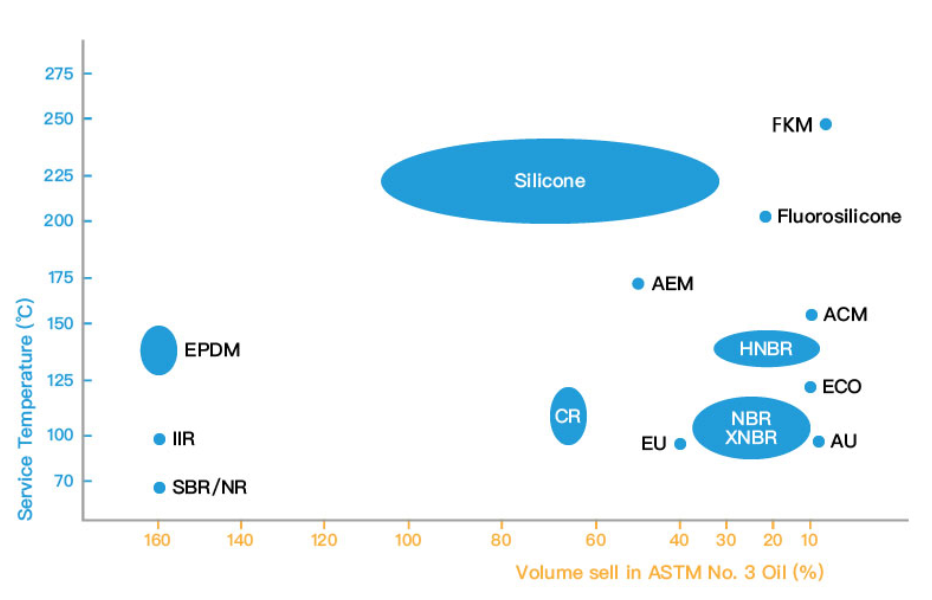
Fluoroelastomer FKM
Fluoroelastomer is a well-known high-performance rubber, especially renowned for its excellent resistance to high temperatures, ozone, weather, oxidation, mineral oils, fuel oils, hydraulic fluids, aromatic hydrocarbons, and many organic solvents and chemicals.
Temperature range:
Static sealing: -26°C to 232°C, short-term up to 275°C. Although it can still be used for a short time at 275°C, its service life will be shortened when the temperature exceeds 250°C.Dynamic sealing: -15°C to 200°C
Due to its outstanding properties of high-temperature resistance, oil resistance, solvent resistance, flame resistance, chemical resistance, and weather resistance, FKM is commonly used in the automotive industry, chemical sector, aerospace, and various industrial applications.
Chloroprene Rubber CR
Chloroprene rubber, one of the first successful synthetic elastomers, was first synthesized by Dupont in 1931. Chloroprene rubber is a copolymer of chloroprene and butadiene. It exhibits excellent resistance to ozone, weather, chemicals, and aging. Additionally, it possesses good mechanical properties, flame resistance, and low-temperature elasticity.
Temperature range: -40°C to 100°C, short-term up to 125°C.
Chloroprene rubber finds applications in a wide range of environments, including automotive, wire and cable sheathing, among many others.
Nitrile Rubber NBR
Nitrile rubber, also known as acrylonitrile-butadiene copolymer (NBR), has a variable content of acrylonitrile in its molecular structure (18% – 50%), which influences the performance of the finished material.
A higher acrylonitrile content improves resistance to lubricating and fuel oils but reduces low-temperature elasticity and permanent compression set. Conversely, lower acrylonitrile content enhances low-temperature resistance but sacrifices oil resistance at high temperatures. A compromise is often achieved by selecting rubber with a medium acrylonitrile content. Compared to other elastomers, nitrile rubber possesses excellent mechanical properties and high wear resistance.
Nitrile rubber has limited weather resistance and ozone resistance. Some special formulations or NBR/PVC blends can address these shortcomings, providing excellent weather resistance, ozone resistance, and resistance to fuel.
Temperature range:
General grade: -40 to 100°C
Low-temperature resistant grade: -55 to 100°C (TR10: -41.5°C)
High-temperature resistant grade: -30 to 125°C (air) -30 to 150°C (oil)
NBR formulations exhibit excellent friction resistance, resistance to non-polar oils, solvent resistance, water resistance, and permeability (higher acrylonitrile content is preferable).
NBR can also be used at low temperatures with diluted acids, alkalis, and salt solvents.
NBR is not suitable for aromatic hydrocarbons, chlorinated hydrocarbons, and polar solvents.
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM)
EPDM is a terpolymer consisting of ethylene, propylene, and a small amount of a third monomer, typically a diene, to provide vulcanization of the rubber. General EPDM rubber exhibits excellent ozone resistance, heat resistance, and weather resistance. It maintains good elasticity at low temperatures and has favorable chemical properties, including resistance to various dilute acids, alkalis, and polar solvents. Additionally, EPDM has excellent insulating properties.
Temperature range:
-55 to 125°C (TR10: -46.1°C), with organic peroxide vulcanization, it can go up to 150°C.
EPDM rubber finds widespread use in the automotive industry, particularly in sealing components for hydraulic fluids based on phosphate esters and brake fluid systems based on ethylene glycol.
For household water applications, rubber components must undergo testing for resistance to chloramine and chlorine. Not all EPDM rubber is suitable for this test; higher saturation EPDM and higher ethylene content exhibit better resistance to chloramine and chlorine erosion. EPDM is also commonly used in hot water or steam applications up to 150°C.
Perfluoroelastomer FFKM
Perfluoroelastomer FFKM, or perfluoroether rubber, is often confused in the market with various suppliers’ trade names. For example, the Kalrez™ rubber series from DuPont is sometimes mistakenly associated with perfluoroether rubber FFKM. In reality, Kalrez™ is a trade name for the manufacturer’s product and not the compound’s name, and the two are not equivalent.
Structurally different from fluororubber FKM, perfluoroelastomer FFKM has carbon atoms in its main chain or side chain bonded to fluorine atoms. It has a higher fluorine content than fluororubber FKM, typically ranging between 74-76%.
Because of its higher fluorine content, perfluoroelastomer FFKM exhibits the best temperature and chemical resistance among all elastomeric materials.
Temperature range: -25 to 250°C
Special grades can maintain sealing properties in environments up to 330°C. It is also resistant to strong acids, alkalis, ethers, ketones, esters, nitrogen-containing compounds, hydrocarbons, alcohols, aldehydes, oils, steam, amine compounds, and various chemical products. Therefore, it is widely used in semiconductor plants or in sealing pipelines in the petrochemical industry.
Perfluoroelastomer FFKM also has excellent gas tightness, with vacuum resistance reaching 1.33X10^-7~1.33X10^-8 pa. However, its drawback is the relatively high cost, and it has always been applied in more demanding environments.
In addition, high-purity perfluoroelastomer, with its extremely low outgassing and no fillers, addresses concerns about contamination of samples or interaction with acids, bases, gases, or plasmas in the environment. It meets various etching process requirements in the semiconductor industry and is widely used. FFKM perfluoroelastomer is extensively employed in the semiconductor industry, petrochemical industry, automotive industry, nuclear energy industry, aerospace equipment, and more. In more challenging environments, its outstanding sealing and tolerance capabilities play a crucial role in collaboration with various industries.
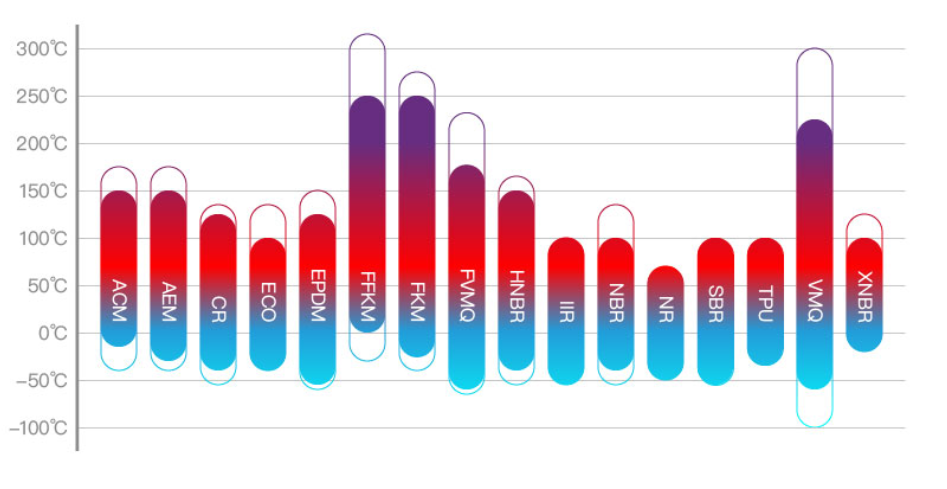
Polyacrylate Rubber ACM, Ethylene Acrylic Ester Rubber AEM, Epichlorohydrin Rubber ECO, Fluorosilicone Rubber FVMQ, Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber HNBR, Butyl Rubber IIR, Natural Rubber NR, Polyester Polyurethane AU, Ether Polyurethane EU, Styrene Butadiene Rubber SBR, Silicone Rubber VMQ, Carboxylated Nitrile Rubber XNBR